The world is full of natural wonders, and one of the most incredible is animal migration. Every year, millions of animals embark on long journeys to breed, feed, or escape harsh weather conditions. From wildebeest crossing the Serengeti to monarch butterflies flying across North America, these migrations are a sight to behold. In this article, we’ll take you on a wildlife road trip, exploring the wonders of animal migration.
The Science of Animal Migration:
Before we hit the road, let’s explore the science behind animal migration. Animals migrate for various reasons, including breeding, feeding, and escaping harsh weather. Some animals, like birds, use celestial cues, such as the position of the sun, to navigate their way. Others, like salmon, rely on their sense of smell to find their way back to their spawning grounds. Scientists are still unraveling the mysteries of animal migration, but one thing is clear: it’s a remarkable feat.
The Best Places to Witness Animal Migration:
There are many places around the world where you can witness animal migration. In Africa, the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem is famous for its wildebeest migration, where over a million wildebeest, zebras, and gazelles travel in search of food and water. In North America, you can witness monarch butterflies migrating from Canada to Mexico, a journey of over 2,000 miles. The Great Barrier Reef is home to the annual coral spawning, where millions of corals release their eggs and sperm into the water.
The Challenges of Animal Migration:
Animal migration is not without its challenges. Many animals face numerous obstacles, including predators, disease, and human activities. Habitat loss and climate change are also posing a significant threat to many migratory species. Scientists and conservationists are working to mitigate these challenges, but much more needs to be done to protect these incredible journeys.
The Importance of Animal Migration:
Animal migration plays a vital role in maintaining the health and biodiversity of ecosystems. Many species rely on the annual influx of nutrients that migrating animals bring, while others depend on the presence of these animals for their survival. For example, the grizzly bears of Alaska rely on the salmon that migrate upriver to spawn. Without these salmon, the bears would struggle to survive.
Most Popular Animal Migrations in the World
Animal migration is a natural phenomenon that occurs all around the world. While there are countless migrations that take place each year, some are more popular than others. Here are some of the most popular animal migrations:
- Wildebeest Migration:
The wildebeest migration in Tanzania and Kenya is one of the most famous animal migrations in the world. Every year, over a million wildebeest, zebras, and gazelles travel across the Serengeti in search of fresh grazing grounds. The migration is a sight to behold, and it’s also one of the largest land migrations on the planet.
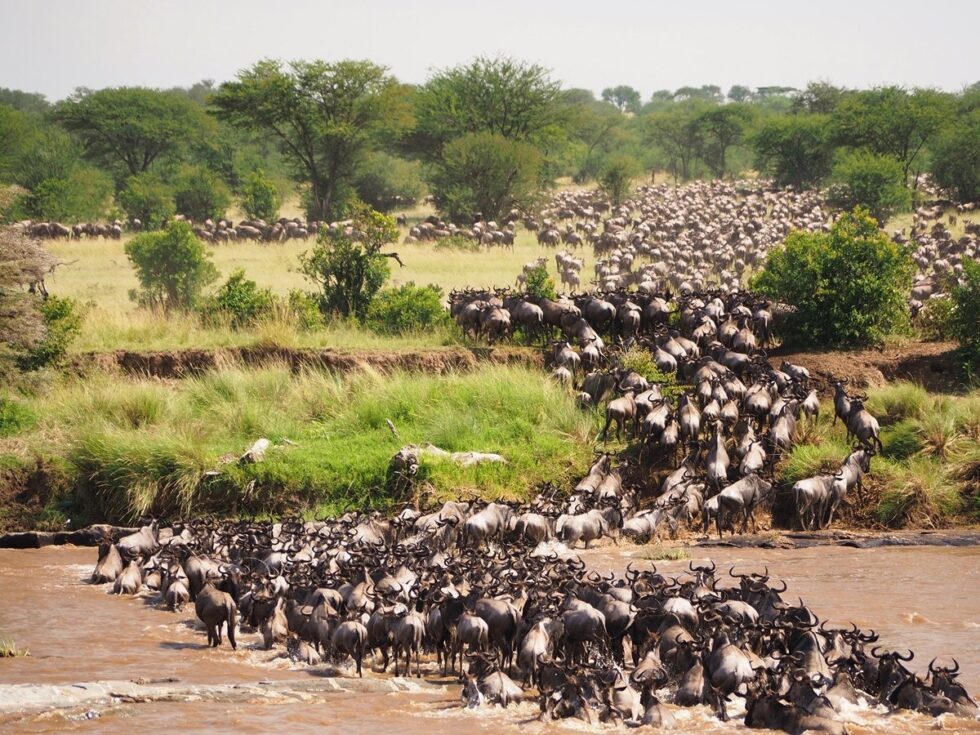

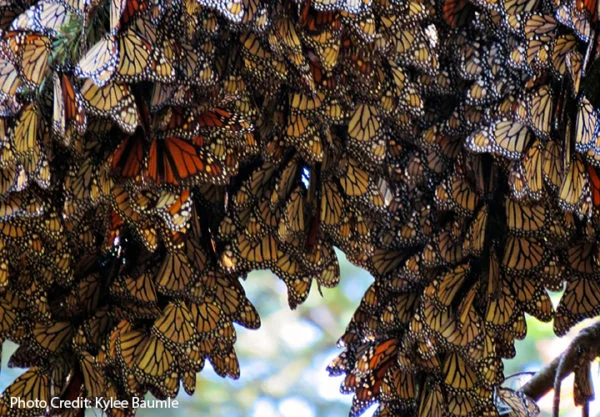
- Monarch Butterfly Migration:
The monarch butterfly migration is another popular migration that takes place every year. Monarch butterflies travel from Canada to Mexico, covering a distance of over 2,000 miles. The migration takes several generations to complete, and it’s one of the most spectacular natural phenomena in North America.

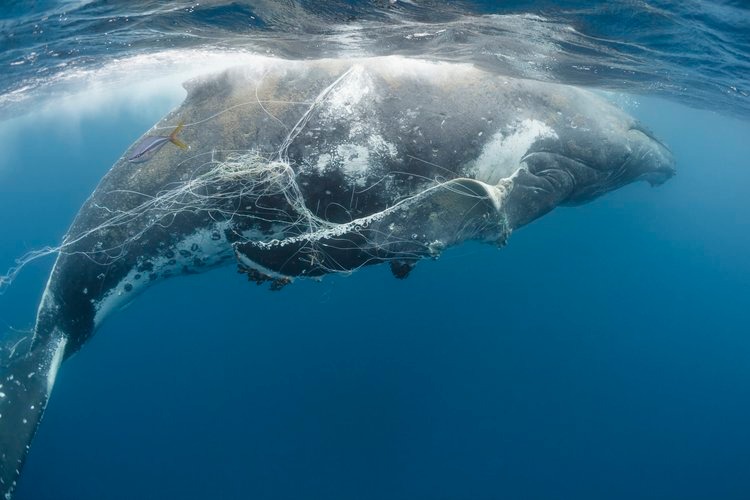
- Humpback Whale Migration:
Humpback whales are known for their long-distance migrations, with some traveling over 6,000 miles from their feeding grounds in the Arctic to their breeding grounds in the tropics. The migration takes place every year, and it’s one of the most popular whale-watching experiences in the world.

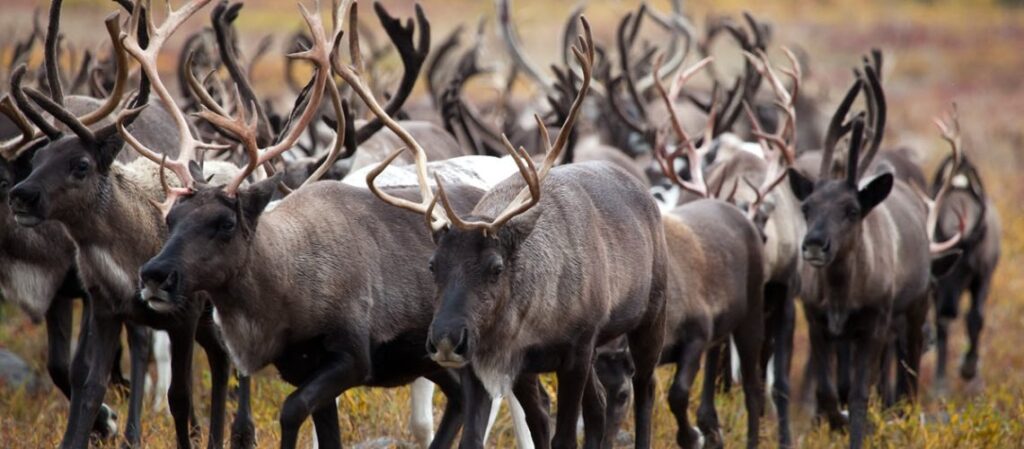
- Caribou Migration:
The caribou migration is one of the most iconic migrations in North America. Every year, hundreds of thousands of caribou travel from their winter feeding grounds in the Arctic to their summer breeding grounds in the tundra. The migration is critical for many predators, including wolves, bears, and eagles, who depend on the caribou for their survival.

- Sardine Run:
The sardine run is an annual migration of sardines along the coast of South Africa. The migration is one of the largest animal migrations in the world, with millions of sardines traveling up the coast in search of warmer waters. The sardine run is also an important food source for many predators, including dolphins, sharks, and seabirds.

These are just a few of the most popular animal migrations in the world. Each year, countless animals embark on long journeys in search of food, water, and breeding grounds. These migrations are a testament to the incredible resilience and adaptability of animals, and they’re a reminder that the natural world is full of wonders that we should cherish and protect. It’s a reminder that the world is full of incredible sights and sounds, and we must do everything in our power to ensure that future generations can experience these wonders too. So pack your bags, hit the road, and witness the magic of animal migration for yourself.
FAQs
- What is animal migration?
Animal migration is the phenomenon where animals travel regularly, usually seasonally, from one location to another, often covering long distances, in search of resources such as food, water, shelter, or for reproduction or other purposes.
- Why do animals migrate?
Animals migrate for various reasons, including changes in weather, availability of food, mating and reproduction, and escaping from unfavorable conditions. Migration allows animals to optimize their chances of survival and reproduction by moving to different habitats or regions with better resources or conditions.
- Which animals migrate?
Many species of animals are known to migrate, including birds, mammals, fish, insects, and even some reptiles and amphibians. Examples of migratory animals include wildebeest, monarch butterflies, salmon, Arctic terns, and humpback whales.
- How do animals navigate during migration?
Animals use various cues and mechanisms to navigate during migration, including celestial cues (such as the position of the sun and stars), geomagnetic cues, visual landmarks, olfactory cues (such as scents and odors), and even their ability to sense the Earth’s magnetic field.
- How far do animals migrate?
The distance animals migrate can vary greatly depending on the species and the specific migration route. Some animals may migrate only a few kilometers, while others may travel thousands of kilometers. For example, the Arctic tern holds the record for the longest migration among birds, with some individuals traveling up to 70,000 kilometers each way between their Arctic breeding grounds and their Antarctic wintering grounds.
- Are there different types of animal migration?
Yes, there are different types of animal migration, including altitudinal migration (where animals move up and down mountains with changing seasons), latitudinal migration (where animals move north or south with changing seasons), and longitudinal migration (where animals move east or west along a particular longitude). There are also partial migrations, where only a portion of the population migrates, and irruptive migrations, where animals migrate irregularly in response to unpredictable changes in environmental conditions.
- What are the challenges and threats to animal migration?
Animal migration faces numerous challenges and threats, including habitat loss, climate change, pollution, barriers to movement (such as roads, fences, and dams), hunting, predation, disease, and human disturbance. These challenges can disrupt or alter migratory patterns, and in some cases, can even lead to declines in populations or species.
- How do scientists study animal migration?
Scientists use various methods to study animal migration, including satellite tracking, radio telemetry, banding or tagging, stable isotope analysis, genetic analysis, and remote sensing technologies. These methods allow researchers to track the movements, behavior, and ecology of migratory animals and better understand their patterns, timing, and ecological roles.
- Can human activities impact animal migration?
Yes, human activities can have significant impacts on animal migration. Habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, hunting, and other human activities can disrupt migratory routes, alter resource availability, and disrupt migratory patterns, leading to negative impacts on migratory animals and their populations. Conservation efforts, such as habitat conservation, wildlife management, and reducing human disturbances, can help protect and conserve migratory species.
- How can we help protect animal migration?
There are several ways individuals and communities can contribute to the conservation of animal migration. These include supporting conservation organizations and initiatives, advocating for policies and regulations that protect migratory species and their habitats, reducing pollution and waste, promoting sustainable land use practices, supporting scientific research and monitoring efforts, and raising awareness about the importance of animal migration and the need for its conservation.